The best way to avoid needlestick and other sharps injuries is to avoid using a sharps device when it is not necessary. The next best way is to use tools to minimize the hazard, such as a safety-engineered device or a needle-syringe holder.
First, identify all sharps devices used in your procedures, then consider the following:
Eliminate sharps
Consider ways to perform the task without a sharps device. Can the same function be performed without a needle or sharp?
Examples:
- Eliminate glass by choosing plastic when possible.
- Use a pipet or similar device to homogenize or mix a solution (rather than using a needle for this purpose)
Additional suggestions for eliminating sharps are provided in the Recommendations sections below.
Substitute sharps
It is estimated that 62-88% of injuries can be avoided through the use of safer devices. Consider selecting a safer device that will accomplish the same result while also lowering your risk of injury.
Examples:
- Use sharp tissue scissors to cut tissue rather than a razor blade for more control.
- Use a plastic gel cutter instead of a razor blade to cut electrophoresis gels.
- Use a blunt needle in place of a sharply pointed one.
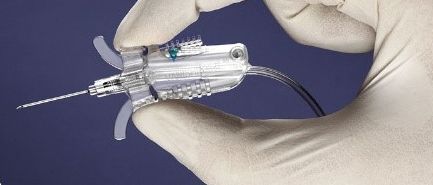
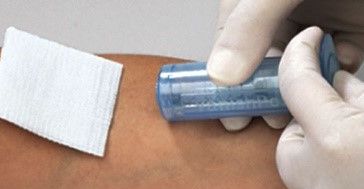
- Safety-engineered devices for needles, syringes, scalpels, blood-draw vacutainer devices, and more can be used in place of the same items without a safety feature. For example, the BD vacutainer blood collection device shown below.
- Luer-lock syringes are highly recommended, to securely screw the needle onto the syringe (vs standard ‘slip tip’ that allows a needle to push onto the end of a syringe).
Additional suggestions for substituting sharps are provided in the Recommendations sections below.
Environmental Health & Safety can recommend safer sharps devices that align with your procedures and desired result.
Prior to beginning a new procedure, develop a standard operating procedure (SOP) that describes:
- Steps to perform the procedure safely
- Tools and instruments that are needed to perform the procedure safely
- Personal protective equipment
- Steps for responding to an accident, exposure or injury
- Safe disposal of needles and other sharps
Resources for developing an SOP include:
- Download an SOP template.
- Refer to the Recommendations sections below.
- Review the Sharps Safety Tools and Resources Presentation or Poster.
- Contact us for recommendations on eliminating sharps and selecting safer devices.
Notes
- If working with human blood or other potentially infectious materials, you must also follow the UW Bloodborne Pathogens Program requirements and have a site-specific exposure control plan. Safer sharps procedures can be incorporated into your Site-Specific Exposure Control Plan.
- A Biological Use Authorization may be needed for use of human source materials in research.
Consult with your supervisor to determine the required and recommended training you must complete prior to beginning work. This includes practicing with less hazardous materials to develop proficiency.
Training may include: